PSA
k8dash is now Skooner! We are currently updating our documentation to reflect this change.
# Overview
Skooner is an open source Kubernetes dashboard that helps you visually understand the concepts of your cluster. Via the dashboard, you can manage your cluster's components and gain an in-depth look at its health and viability.
# Skooner at a glance
Skooner was first released in March 2019.
It has received over 660 GitHub stars and over 1.1 million Docker Hub pulls.
In May, 2020, Indeed Engineering adopted the Skooner project. Skooner is installed as a standard at Indeed.
Please star the project at github.com/skooner-k8s/skooner. (opens new window)
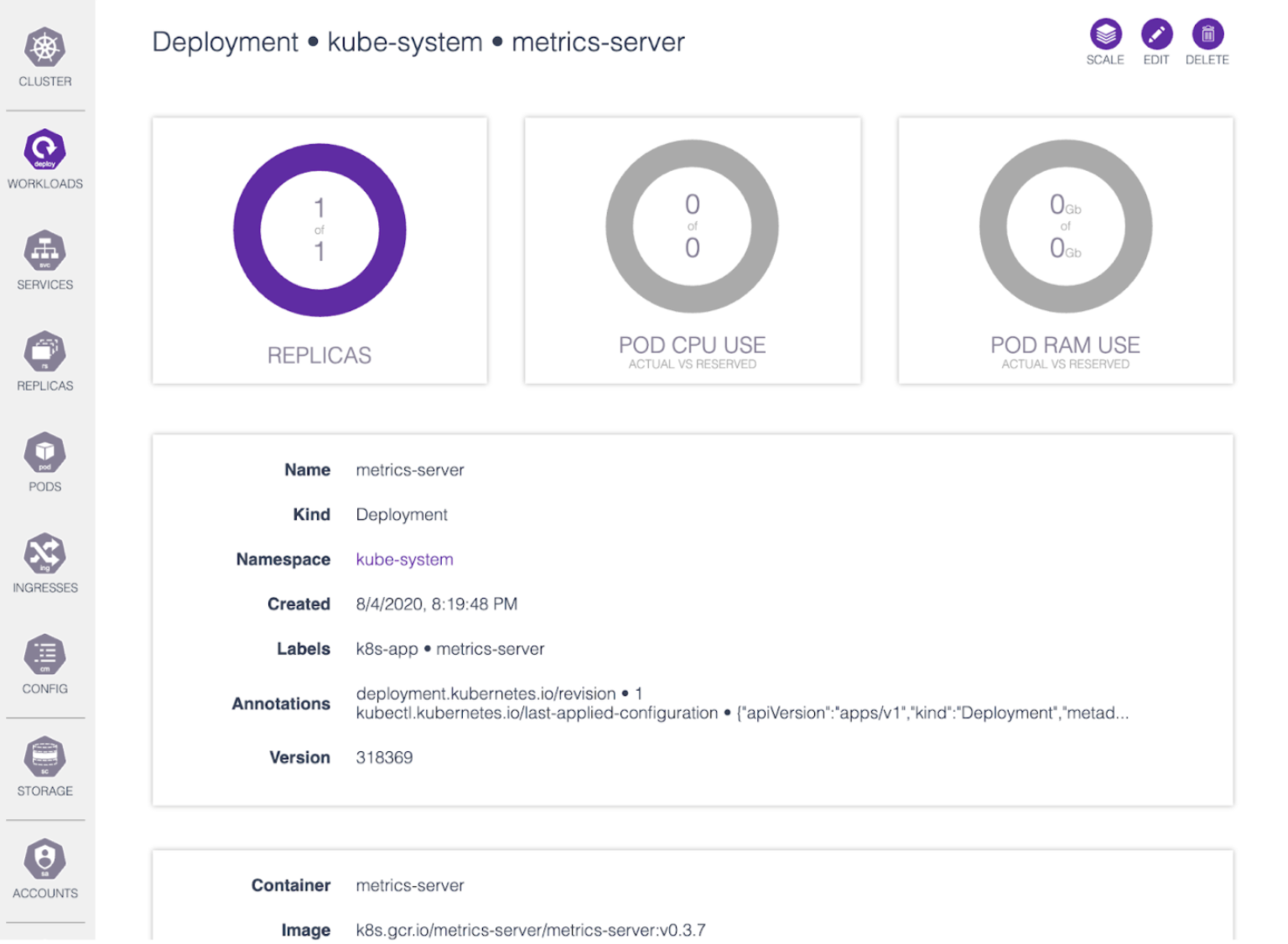
# Skooner desktop
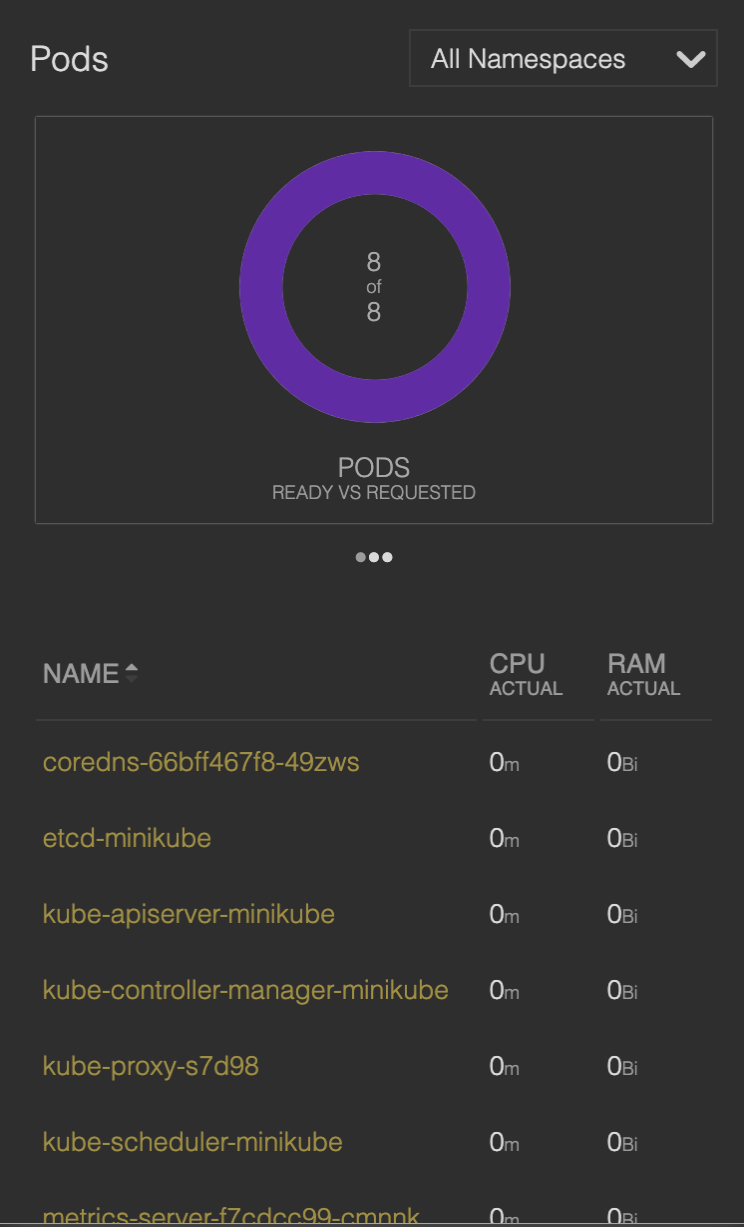
# Skooner mobile
# Skooner features
With Skooner, you can
- fully manage your cluster, including namespaces, nodes, pods, replica sets, deployments, storage, RBAC, etc.
- learn the status of components, which pods are deployed, and which pods or deployments use the most resources
- benefit from a Kubernetes dashboard that automatically refreshes and updates in real time
- quickly view your cluster’s health via real-time charts that help you track poorly performing resources
- monitor your cluster while on-the-go via the 100% responsive UI that runs on your phone or tablet
- get started in as little as a minute using the provided YAML
- update and scale your cluster via the Resource YAML Editor, which includes inline API docs that describe each field
- employ a Simple Open ID integration with no special proxies required
If you’re already using OIDC to secure your cluster, Skooner makes extending this to your dashboards easy. Configure 2-3 environment variables and you’re up and running. No special authenticating proxies or other complicated configurations are required.
# Why Skooner?
| Feature | Skooner | Octant | Lens | k9s | Default Web UI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | |||||
| Cluster management | x | x | x | x | x |
| Mobile optimized | x | ||||
| x | x | x | |||
| x | |||||
| x | x | x | |||
| RBAC Support | x | x | x | x | x |
| Plugin Functionality | x | x | x | ||
| Metrics | x | x | x | x (not real time) |
The following is a deeper dive into the open source Kubernetes dashboards listed above:
Default Web UI (opens new window)GitHub (opens new window)
The default Kubernetes web UI allows you to perform cluster management without needing to download additional software. Limitations include
- no real-time updates
- not optimized for mobile
- more complicated installation that creates many more Kubernetes objects
Additionally, the Kubernetes built-in dashboard only supports bearer token logins out of the box. Support for OIDC requires additional configuration, generally by setting up an authenticating proxy (a separate piece of software).
K9s (opens new window)(GitHub) (opens new window)
K9s is a command line interface with ASCII art. It provides a terminal UI to interact with your Kubernetes clusters. The aim of the K9s project is to make it easier to navigate, observe, and manage your applications in the wild. K9s continually watches Kubernetes for changes and offers subsequent commands to interact with your observed resources.
Octant (opens new window)(GitHub) (opens new window)
Octant is an extensible platform that features real-time updates and works as an installed desktop application. Octant helps you understand the complexity of Kubernetes clusters through a combination of introspective tooling, cluster navigation, and object management. Octant’s plug-in system provides additional functionality through gRPC. Because Octant is an installed desktop application, you can’t share links with others.
Lens (opens new window)(GitHub) (opens new window)
Lens, created by VMware, is an installed desktop application. Lens bills itself as a Kubernetes IDE and offers real-time cluster-state visualization and multi-cluster management for hundreds of clusters. With Lens, you can manage extra-large clusters (up to 25,000 pods). Prometheus powers resource utilization charts and trends with history. Lens also supports terminal access to nodes and containers. Because Lens is an installed desktop application, however, you can’t share links with others.



